A trust is a tool for tax planning, protection of assets and their transfer by inheritance. The main misconception is that a trust is perceived as a legal entity, that is, a specific type of company. In fact, a trust is a special form of property contractual relations.
Our company is highly qualified specialists in the field of establishment and further support of businesses. We work with all types of commercial structures and offer an extensive range of corporate services, in particular for the registration of trusts.
Table of Contents
Introduction to Trusts as Financial Tools
In such an agreement there is one more mandatory element – the assets that constitute the subject of the trust. Without assets, a trust cannot exist.
When creating a trust, full ownership of assets is split into two components:
- legal ownership (right of ownership and control), which is transferred to the Trustee;
- beneficial ownership (the right to receive benefits), which passes to the Beneficiary.
Thanks to this split, it is impossible for the Beneficiary to make a tax claim against the trust assets, since he does not formally own or control them. The Beneficiary’s tax obligations arise only in connection with the income or assets actually received. Trusts can be set up for both charitable purposes and for private purposes.
Types of Trusts and Functions
They are often used to transfer inheritances, manage the assets of minor children or individuals who are unable to manage their own finances, and to ensure the security of property.
Trusts are used for:
- transfer of inheritance (no need to pay inheritance tax, information about trust participants and their names may not be disclosed);
- preserving property from waste (inability to manage money) – to provide income and capital to beneficiaries (for example, the children of the founder, in the event of his death) until they reach a certain age;
- joint ownership of property that is difficult to divide;
- charity; corporate pension payments;
- hiding property and receiving benefits, reducing the tax rate, avoiding creditors (formally, the property no longer belongs to the founder).
The following categories of these agreements are distinguished.
- Revocable or irrevocable. If the trust is revocable, then its Settlor can reclaim the transferred assets at any time. Such a trust is usually useless because a court may find it fraudulent. If the trust is irrevocable, then the Settlor will not be able to remove assets from it.
- Fixed or discretionary. In a fixed trust, the distribution of income and assets is made based on the express instructions of the Settlor, and the Beneficiaries are listed by name.
- Beneficial or target. If there is a Beneficiary in the trust, then such trust is beneficial. This type of trust is considered “classic” and is used most often. There are no beneficiaries in a purpose trust – it is created to achieve a certain goal.
- Asset Protection Trust. This name is rather arbitrary, since asset protection is provided by all types of trusts.
- International. It is not a separate variety. The name is explained by the fact that the elements of such a trust are tied to different countries.
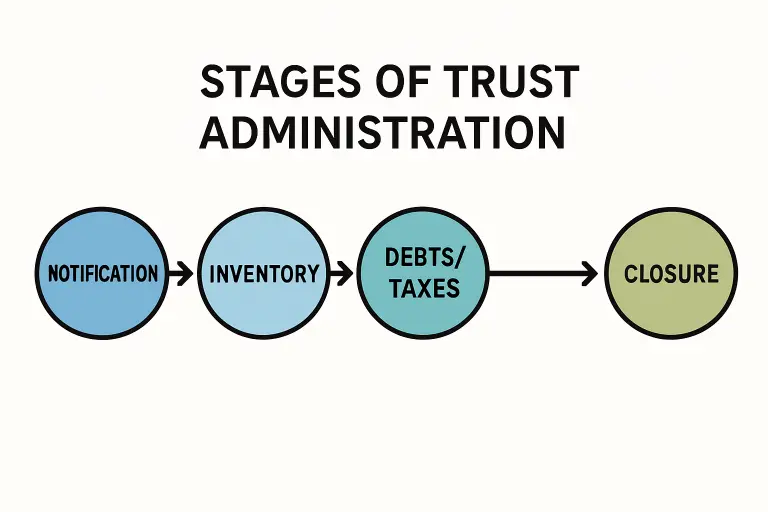
Best Practices for Efficient Trust Administration
The benefits of using trusts include the following.
- Confidentiality. Trusts are generally not public documents and do not require public registration. Information about the trust and its assets can only be accessed by the manager and the beneficiary.
- Limitation of taxes. Some types of trusts may be subject to income tax, but this does not usually apply to trusts established for charitable purposes or for private purposes. In addition, some types of trusts can be used to reduce tax liability and manage your tax burden.
- Flexibility. Trusts can be set up with various terms and conditions to reflect the individual needs and wants of the beneficiaries. This may include conditions related to age, education, health, financial status, etc.
- Property protection. Trusts can provide protection for assets from creditors, lawsuits, and other types of legal harassment.
- Property management. Trust managers are professional financial managers who can ensure the effective management of the assets held in the trust.
Under trust law, a trust has no shareholders or members. The founder of a trust, transferring his/her assets to the trust upon its establishment, legally completely renounces all property rights (ownership rights) to the transferred property. Moreover, there are no vested interests in the trust or its assets that can be taken away by a court order.
The absence of legally secured rights for the founder of the trust presents the possibility of protecting the property transferred to the trust from collection for the debts of the founder or beneficiary of the trust.
Thus, how are trusts managed and which are trust management complexities?
- First way.
The founder has the right to draw up (or draw up annually) a letter of wishes in which he/she can indicate the beneficiaries of the trust (parents, spouses, children), as well as the conditions for the payment of funds from the trust to them, as well as the conditions for the complete termination of the trust and the conditions for the distribution of its assets among the beneficiaries. In this case trust tax implications will be lower.
- Second way is using Orders.
Articles of Association may provide special provisions that the Settlor may give legally binding instructions to the Trust. In this case, the Trustee will in all cases be obliged to comply with all orders of the Founder.
- Third method is to appoint the Founder as an Investment Advisor to the fund.
Another possible way in which the Settlor can control the assets of the Trust is by appointing the Settlor as the Trust’s Investment Advisor. For this purpose, the Trust, when concluding a banking/brokerage service agreement, appoints the Founder as a person authorized to give orders for the purchase and sale of assets. Thus, the Founder has the opportunity to directly and promptly manage the assets of the trust, without resorting to writing letters of wishes and coordinating his actions with the Protector.
Planning for trust administration can include a variety of services, such as:
- legal advice;
- accounting support;
- tax support;
- financial and investment management;
- property management.
Depending on the needs and requirements of the client, trust management can be carried out both within one jurisdiction and on an international scale.
For efficient trust administration, it is important to choose a reliable and experienced manager or administrator who will provide effective and transparent management in the interests of the beneficiaries. It is also necessary to take into account legal and tax aspects in the relevant jurisdictions in order to avoid possible risks and inconsistencies with local legislation.
The most interesting point is the case when funds are transferred to the trust for working on stock exchanges with securities or cryptocurrency. In this case, the trust founder wants to be able to quickly manage money, and in some cases, full access to it.
Trust management strategies need to contain mechanisms for insuring risks and transferring the insurance policy to the custody of a trust company; it is always necessary, but it is not always economically justified. In any case, you need to start with a consultation.
Our company is ready to provide you with trust administration best practices and comprehensive advice on issues related to the management of trusts and the conclusion of such contractual relations. Our specialists take an individual approach to each case and make every effort to achieve effective results for each client. Contact us now.
The article’s author is Denys Chernyshov – founder and CEO of the globally-famous organization Eternity Law International.









































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0