Table of Contents
Biomedical Research Minor at UCLA
Molecular Cell and Developmental Biology
Taking a Biomedical Research Minor is a fantastic way to enhance your knowledge of the life sciences. It will not only help you get involved with laboratory research early on, it will also train you in science and social issues. The Biomedical Research Minor, also known as MCDB, is designed to teach you the many aspects of the life sciences and prepare you for future careers.
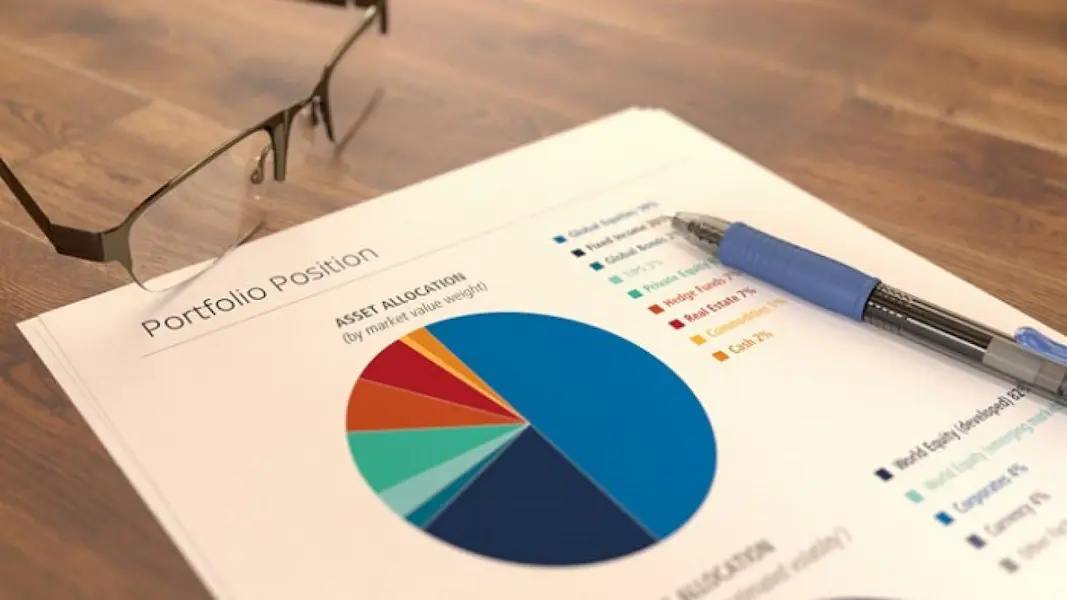
The MCDB program offers students the opportunity to study the science of molecular, cell, and developmental biology. The curriculum is a mix of core and elective courses, and is updated annually to reflect new developments and discoveries in the field. The Biomedical Research Minor consists of five core courses.
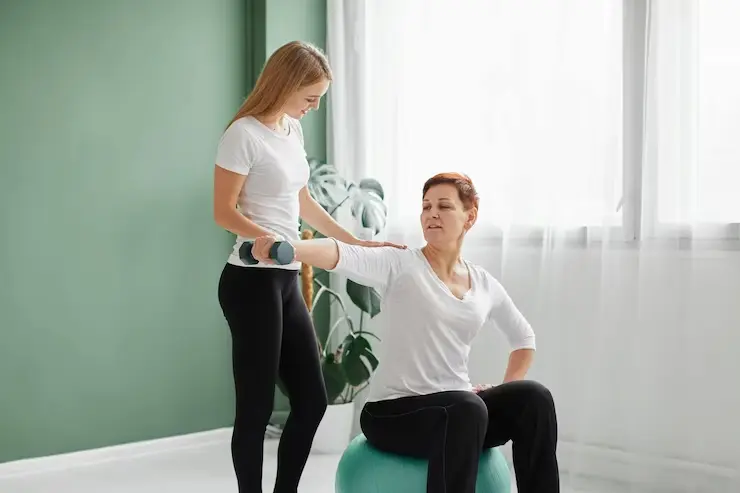
The MCDB program also offers students the opportunity to take advantage of the latest research and technology developments by arranging to do a four-quarter research project at a College or Medical School lab. Students take courses in science and technology policy, history or philosophy of science, and analysis of research literature. The most notable course is MCDB 370, a course designed to give students hands-on research experience. Throughout their time at UCLA, students will have the opportunity to engage in a number of simulated research projects, including experiments in cell biology and cellular signaling. The minor may also lead to a research internship.
While there is no guarantee that a student will find a research opportunity at UCLA, the odds are very high. Students are paired with scientists and research technicians who are well-trained in executing complex laboratory experiments. The MCDB program also boasts a number of exciting upper-division courses designed to give students an appreciation of the work of other scientists in the field.
The MCDB program also offers a number of elective courses, many of which are geared toward the student’s specific interests and skill sets. The Biomedical Research Minor combines the MCDB program’s core curriculum with elective courses designed to build on the foundations of the MCDB program. The MCDB program also has a strong record of providing students with the scientific training and research experience necessary for a rewarding career in the life sciences.
Biomedical Research: Concept and Strategies
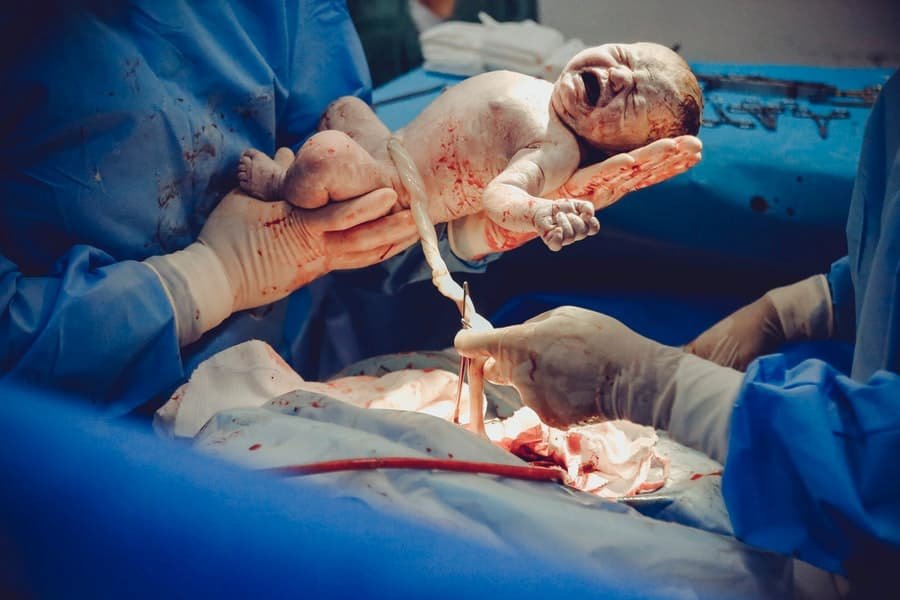
During the 20th century, the field of biomedical research developed. It included several subdisciplines of medicine and biology, spanning from basic research on single molecules to populations of human subjects. The field also includes the study of molecular pathology and transfusion science.
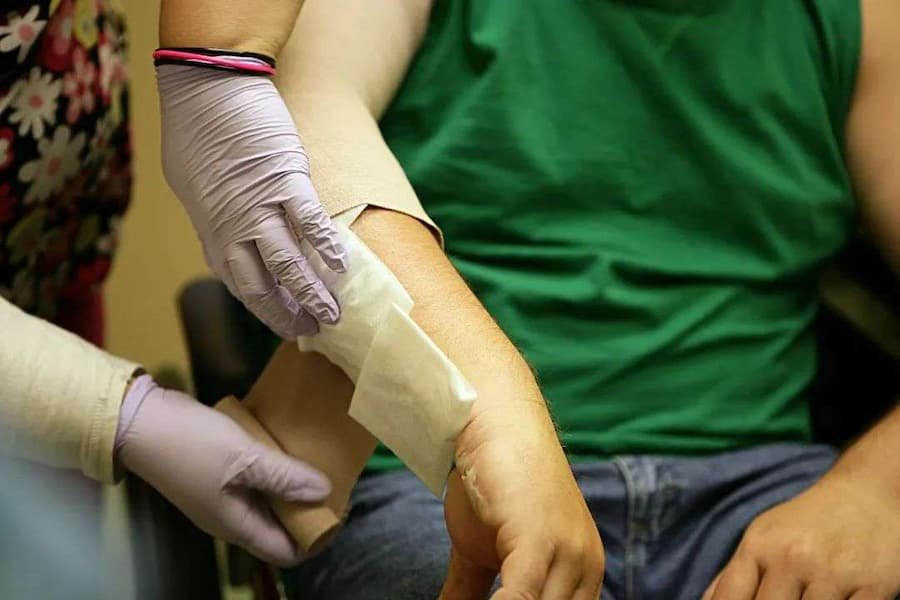
Research on human subjects is often conducted at academic health centers, hospital-based research centers, or both. It can have a significant impact on understanding human biology. It also often has a direct impact on health care. Often, the studies are performed on small groups of people initially, then expanded after safety is demonstrated. It often involves research on single molecules, such as a DNA fragment, or a single cell. Some biomedical scientists also have a medical degree.
The majority of researchers who perform research on human subjects are motivated by the potential applications of their work. This can include clinical trials, which are phased studies using human volunteers to test the safety of products. However, some studies are not FDA-regulated.
Biomedical research is an integral part of the public health infrastructure. Research that creates new knowledge is essential for the benefits of society. However, it can become a divisive issue within the academic biomedical community. It is important to eliminate this unnecessary distinction between basic and translational biomedical research. This would promote better use of scientific resources and could improve the effectiveness of the scientific process.
The biomedical research community was faced with stress during the 1990s and early 2000s. During this time, hyper-competition and inequality made the workforce vulnerable. Many researchers believed that the age-old distinction between basic and applied research was still relevant.
In the late 1990s, the U.S. government stepped in to expand the budget for biomedical and health research. The funding was directed at translating the research into clinical application. This led to the creation of new research infrastructure and increased demand for Ph.D.s seeking support from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). However, the increased demand for Ph.D.s and the limited government funds created a divisive effect in the academic biomedical community.










































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































0